Fermentation is the process by which beer, wine, whiskey, and other alcoholic beverages are produced. Fruit, sugar, or starch bearing materials are put into solution with water and ‘yeast are added. Yeast are tiny organisms that eat the sugar and produce CO2 and alcohol as bodily wastes. The yeast reproduce very rapidly and more and more yeast eat the sugar and produce alcohol and CO2. They soon raise the alcohol level in their environment above 10%, which causes the yeast to stop metabolizing.
Indoor hobbyists have used the fermentation method for a few years now, and it is recognized as a reliable and inexpensive way to manufacture CO2.
Homebrew
Some hobbyists use the fermentation system because they like the second hobby
-
home beer and wine making! A few five gallon jugs of quality homebrew, or a few wooden casks of wine, can greatly enhance the output of a growing chamber. With inexpensive and accurate CO2 test kits now available, it is possible for a hobbyist to determine the amount of brew that must be working to keep his grow room at the desired ppm of
CO2.
There are many books on home beer and wine making, and
almost every city usually has a store that sells beer and wine making
supplies, lithe supplies are not available in your area, check the Yellow
Pages or mail order companies.
Simple Small Scale
Fermentation
If the fermentation method meets your needs as a system of
CO2 enhancement, but you have no desire to produce drinking alcohol, the
process is very simple. Sugar, water, and yeast from the grocery store are
used to make a simple brew that produces CO2 at a fairly regular rate for
about 3 to 4 days. At this time the spent solution is dumped and a new
brew started.
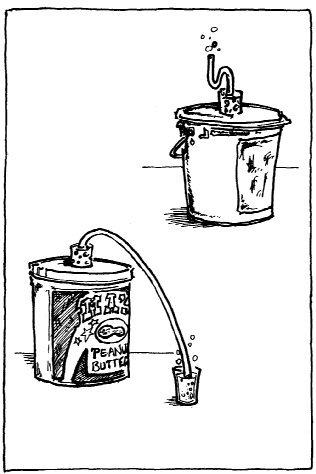
Gallon Jug CO2 Fermentation
- Make a starter mixture of a half cup of sugar and a
pinch of yeast (distiller’s yeast is best) in 12 ounces of water. Set
this in a warm place until it starts bubbling.
- Make a mixture of two pounds of sugar in six quarts of
water in a three or four gallon plastic jug.
- Poke a small hole in the top of the cap and put the
bubbling froth in the grow room. Although the simple hole poked in
the top of a milk jug cap works fine most of the time, many growers follow
the advice of home beer brewers and attach a fermentation lock to the top
of the mixture. This equipment serves two purposes. It bubbles the CO2
through water so that the rate of production is easily observed and
calculated, and it prevents contaminants from entering the fermentation
mixture.
- When the bubbling slows down after about three days, add a bit of the old mixture to another fresh batch of sugar water, and discard the old mixture. The new one should start working in a few hours. Remember to keep the temperature below 95 degrees and above 80 degrees. (See drawing.)
Larger Scale, Continuous Batch
Fermentation
Using approximately the same
ratios of sugar and water as described above, a large scale fermentation can
be kept going for up to two months. Start with a large tub, tank, or trash
can. Add a gallon of sugar water every day or two and see how high it
keeps the CO2 levels in the grow room. Be sure to leave lots of
room for additional liquid as the tank fills. Remember that cleanliness, and a
good air lock, are the keys to a long-lasting fermentation. (See
drawing.)
CO2 from sugar is an expensive method of production. If
the
brew is used for consumption, or the alcohol is to be
distilled for
fuel, it makes sense economically.
Advantages of
Fermentation
- The system can be set up very inexpensively.
- The process uses common materials.
- Utilization of fermentation to make CO2 fora growth
chamber can provide home brewed beer, wine or fuel as a by-product
of the process.
- The process uses no heat, flame, gas, flammable liquid, or electricity.
Disadvantages of
Fermentation
- The process can get messy.
- The fermentation process can present an odor problem.
- Continuous generation is not as efficient as periodic
injection of an amount sufficient to treat the entire room in one
rapid release.
- It is difficult to achieve fairly uniform CO2 levels from one day to the next. This is because there is fluctuation in the amount of CO2 generated at different phases of the fermentation, and there are a myriad of factors which can effect each fermentation, causing different levels of CO2 to be produced.
Floral Beer
Floral
Beer is a phenomenon with a rather limited but enthusiastic
following among the scientific/horticultural community around
California's Bay Area and Silicon Valley.
It is made by soaking aromatic
plants in homemade beer while the beer is brewing. The alcohol in the beer
removes the aromatic essences of the flowers or leaves being soaked, and
imparts unusual qualities to the beer.
In some recipes the water-soluble
chlorophyll and pigments of the flowers or leaves being soaked are
removed prior to the beer making process.
The plant material is first soaked
for about 8 hours in cold water, with a minimum of agitation. It is then
rinsed, the flowers are dried and then added to the batch of beer in a
large cheesecloth sack. The soaking and rinse water are discarded. The
sack is allowed to remain in the brew during the entire process. It is
removed prior to
bottling.